Proof of Concept (POC) is an approach for verifying the viability of an initial idea and testing its feasibility for its practical development. It is logical proof that the solution to a particular problem is possible to implement.
Digging deeper into the topic, in this article, we will explain what a proof of concept is, where it is used, discuss POC in different fields, analyze the differences between POC, prototype, pilot, and MVP, and evaluate who can benefit from a POC report.
We also explore how to write and present a proof of concept report and go through some popular examples of proof of concept used to validate an idea before developing a solution.
Before starting with the article, check out our Free Proof of Concept Template compatible with PowerPoint and Google Slides.
What is Proof of Concept (POC)?
A proof of concept (POC) is a verification methodology that analyzes whether an idea can be turned into reality. It is used in the initial stage of a product lifecycle and determines its feasibility.
It serves as proof to potential investors, managers, and other stakeholders that the proposed idea, product, or system can work in real life to gain their approval and take it to the commercialization stage.
Why is Proof of Concept Used?
1. To Attract Investors
A proof of concept shows investors that their investment would be put towards an idea that works. It gives them proof that the project idea is financially sound and that the team behind it has researched and planned everything for taking it to the next stage and making it work.
2. To Foresee Limitations
Every idea has its limitations and needs to be evaluated before proceeding. POC helps analyze the scalability of the concept and determines if it can accommodate the organization’s growth. An example of this is building an automated system for collecting and analyzing customer data. How much data would the system be able to handle? Could it be scaled in the future to handle the additional volume?
3. To Prepare for Possible Challenges
Possible challenges can be addressed using POC as it provides a clear picture of issues and obstacles that can arise before starting the project. Whether it’s the development or marketing phase of the project, POC can help identify solutions to any problems, highlight risks, and help prepare for possible challenges. This helps save money in the long run and increases the project’s chances of commercial success.
POC in Software Development and Information Technology
Proof-of-Concept (POC) in software development and information technology (IT) refers to the successful demonstration of a system and its practical use in real life. It determines the feasibility of the product from a technological perspective, where technical issues and system integration problems are highlighted, and their solutions are presented while making sure user requirements are met.
The POC includes detailed documentation of the processes, objectives and specific roles that the team plays during the development of the product. Project managers also use POC to figure out any loopholes that could prevent the successful use of the software and ensure that the system runs smoothly without errors.
POC in Business Development
In business development, POC is used to determine the financial viability of their product. Startups extensively research and review their revenue model, their product offering, marketing strategies, product development cost, and financial projections, both short and long-term, to indicate its feasibility.
Besides that, POC is also an important part of existing business used to evaluate internal proposed acquisitions and new project ideas. It offers them sufficient evidence that the product can be taken to the commercialization stage and determines the return on investment (ROI).
POC in Blockchain
POC in blockchain verifies that the project idea has real-world potential and feasibility. It determines whether the proposed idea will function as planned and help gauge the applicability of blockchain technology to an idea.
It is basically a straw-man design for determining the success of a blockchain application and validates the idea of moving forward with its development. Organizations, startups, and governments use POC to save time and money by proving that an idea will work before committing to the project.
POC in Other Industries
Besides software development, business, and blockchain, POC is also used in other industries for gaining investments and validating ideas before proceeding with production.
In film-making industries, for example, directors often create a short proof of concept film to show production companies what the film would be about.
Also, in healthcare, pharmaceutical researchers do a proof of concept study for drug discovery and development processes, validating its effects, and also determining its side effects, before commercialization.
Other than that, in cyber security POC exploits are used to identify system vulnerabilities and protect against cyberattacks. This is a proactive approach to determining weak points in the system and mitigating issues to enhance the overall cyber security protocol.
Differences Between POC, Prototype, and MVP
Besides POC, prototypes, MVP, and pilot launches are also used to validate ideas, test product feasibility, and analyze customer feedback.
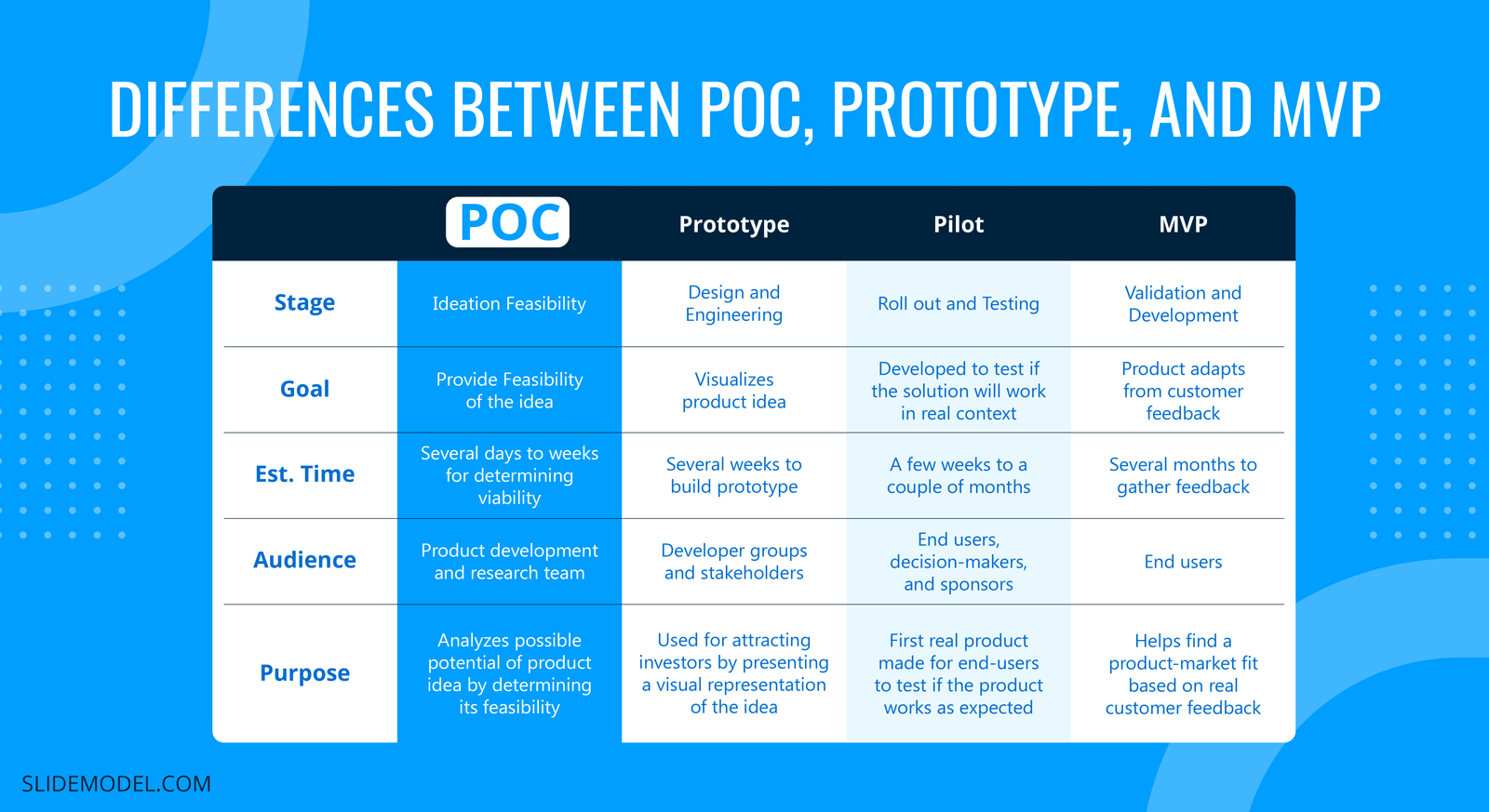
POC comes first before the rest and helps determine their success before one actually commits to an idea.
| POC | Prototype | Pilot | MVP | |
| Stage | Ideation Feasibility | Design and Engineering | Roll out and Testing | Validation and Development |
| Goal | Provide Feasibility of the idea | Visualizes product idea | Developed to test if the solution will work in real context | Product adapts from customer feedback |
| Est. Time | Several days to weeks for determining viability | Several weeks to build prototype | A few weeks to a couple of months | Several months to gather feedback |
| Audience | Product development and research team | Developer groups and stakeholders | End users, decision-makers, and sponsors | End users |
| Purpose | Analyzes possible potential of product idea by determining its feasibility | Used for attracting investors by presenting a visual representation of the idea | First real product made for end-users to test if the product works as expected | Helps find a product-market fit based on real customer feedback |
Who can Benefit from Proof of Concept?
1. Project Managers
POC helps project managers in implementing their proposed idea by determining the possible risks and obstacles. It enables them to increase the project’s chances of success as they evaluate how to build and scale the idea and take it to the next stage.
2. Project Leaders
Project leaders can use POC to verify the feasibility of an idea, determine its scalability and reduce costs associated with the product. It helps them analyze the feasibility of the product on a mass production level and determine workflow standardization and the required resources.
3. Stakeholders
Stakeholders need proof before approving any idea that it will be profitable for the company. It is a rich form of initial analysis that helps stakeholders assess the usability and feasibility of the idea before they take any decision. The POC gives them enough evidence via visuals, data, and illustrations to help them reach their final decision.
How to Write a Proof of Concept Report?
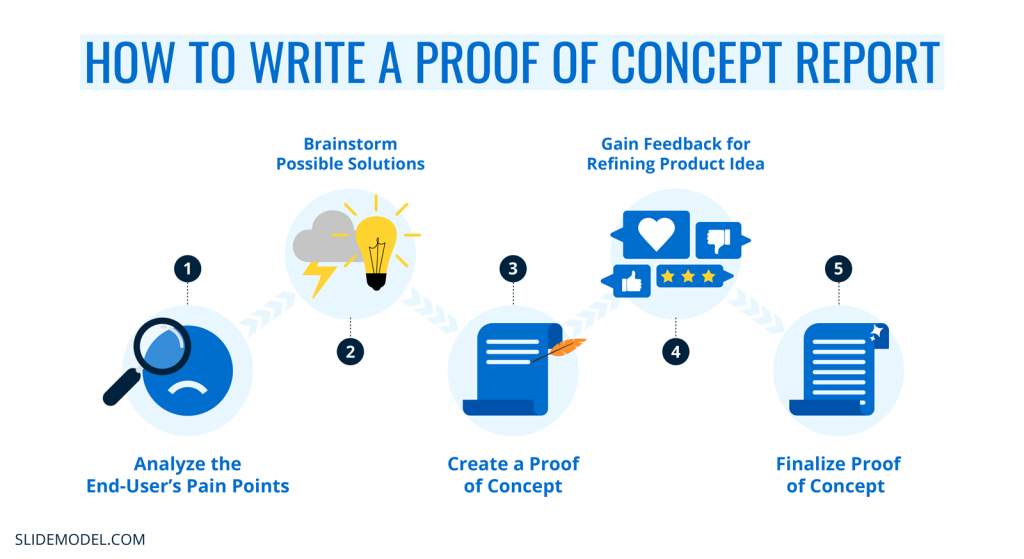
1. Analyze the End-User’s Pain Points
For writing a proof of concept report, it is essential to understand the audience’s pain points. Analyze what the end-users need to solve their problem by looking through customer feedback, surveys, and market research. List the pain points that the proposed product should solve or minimize.
2. Brainstorm Possible Solutions
After analyzing and listing the end-users pain points, brainstorm possible solutions. Determine the feasibility, cost, and timeline of each solution by comparing them and figuring out the best solutions for the audience. As a plus point, gather feedback from potential users about the solutions to figure out how they can be improved.
3. Create a Proof of Concept
Next step is to create the proof of concept report from the data gathered in the last step. The product that addresses the users’ pain points needs to be tested for feasibility and to determine if the proposed product solves the audience’s problems.
4. Gain Feedback for Refining Product Idea
The proof of concept can be presented to users to refine the product idea and identify which areas need more fine-tuning. Gather valuable input for making improvements and develop a final proof of concept report.
5. Finalize Proof of Concept
Finalize the proof of concept by clearly defining the product’s criteria for success, documentation for how the POC will be carried out, and an evaluation component. The POC should include the functionalities of the product, its features, benefits, and the problem it solves for end-users.
Moreover, the cost, timeline, and resources required need to be presented to stakeholders as well, so they can make their final decision. In case the POC is approved, also have a proposal ready for how the team plans to move forward by listing the next step towards product development.
How to Present a Proof of Concept?
After writing a proof of concept report, it needs to be presented to stakeholders for approval and moving on to the next stage in product development. Here are some elements to ensure the POC presentation goes well and has the chance to be approved by the interested parties.
1. Start By Defining the Success Criteria
When the need for a solution is identified, a set of metrics or success criteria determines the concept’s feasibility. These are the standards that ensure that the product will help the end-users solve their problems. The POC presentation requires clearly defined success metrics based on the customer’s need for a solution.
2. Provide Estimated Timeline
A POC should have an estimated duration for the completion of the final product. The estimation should be clearly presented for each stage of the product development, so the investors know how much the team is involved and how much time it will take for the product to commercialize.
3. Establish Scope of the POC
The scope of the project needs to be established in the POC presentation to show how the product will help end-users in solving their problem. A proper evaluation is required to determine the value and scope of the product which helps investors see the feasibility of the proposed idea.
4. Determine Required Resources
In the POC presentation, determine the required resources that would be used in product development. From choosing the personnel with the right skills required to execute the product development plans to the number of material resources required, defining a set of resources is crucial for clients to know that the proposed idea is viable.
5. Present Roadmap for Next Steps
Lastly, presenting a roadmap of the next steps is crucial to let the clients, stakeholders, and investors know that the team is serious about building the product and getting it to the market. The next step would be to build a prototype for testing the solution, gain additional feedback through a pilot launch, and develop a minimum viable product (MVP).
Examples of POC
1. Leonardo Da Vinci Armoured Car
Leonardo Davinci Armoured car is a historical example of proof of concept used in modern warfare nowadays. He designed an armored car that could move in all directions while also being equipped with multiple weapons.

Da Vinci solved the problem of the army driving safely in all directions and scattering the opposing force using the weapons. The car is covered with a protective cover like a turtle’s shell that is reinforced with metal plates and a sighting turret on top for coordination. It features a number of light cannons equipped on a circular platform with wheels that can move in 360 degrees to attack the enemy from all sides.
2. The Bitcoin Whitepaper,
A popular poof of concept example, is the Bitcoin Whitepaper. Satoshi Nakamoto published it in 2008, where he proposed a solution with a detailed explanation of how blockchain will work, and how bitcoin can be good for society.

The published paper serves as a proof of concept, where the public adopted its use, and a whole new payment and trading industry was created. He addressed the problem financial transactions face and how bitcoin can eliminate that, thus gaining the public’s confidence.
3. The Walmart Case Study
Another great and recent example of proof of concept is Walmart’s application of blockchain technology in their food supply chain. Partnering with IBM, Walmart aimed to improve the traceability of their food products to react to food-borne disease outbreaks quickly.
For this, they ran two proof of concept projects, one in the US for tracing mangoes and one in China for tracing pork supply. The blockchain-powered solutions proved to be a success, made the tracing process much faster, and helped discover the origin of their supply in seconds.
The POC gave Walmart a viable solution for high-risk situations and helped them decide that the investment in blockchain was worth it.
Proof of Concept Templates
Access to different Proof of Concept Templates that will allow you to graphically capture the process of bringing an idea to reality and validate it in your target market.
Conclusion
A proof of concept is not an optional activity but a crucial exercise for technology startups and businesses for getting insight into the viability and feasibility of their idea.
New ideas often fail to gain approval or succeed because they don’t present a POC, are confident that their idea is the best out there, and go straight to commercialization, where they lose their precious time, money, and other resources.
Using a POC, startups realize how they can best help address their user’s needs. Limitations and risks come to light that can be overcome in the initial stages rather than after the launch, which could result in loss of customers.
POC is all about creating a viable product that helps customers solve their problems in the best way possible and yields a high ROI for investors.