
QR codes have been around even before major internet platforms were even born. Before Google Search, Facebook or responsive UI designs taking the Internet by storm, the QR code was being used for high-speed component scanning during vehicle manufacturing. However, it wasn’t until the advent of smartphones that people began to recognize and widely use QR codes. Today, they are used from app installs and login session authentication to checking product information at convenient stores and even for making digital payments. In the wake of COVID-19 and contactless shopping, QR codes have experienced a boom. In this article, we will explain all you need to know about the different types of QR codes, their application and the boom of QR codes in times of COVID-19.
What is a QR Code?
First introduced in 1994 in the automotive industry in Japan, a Quick Response code or just QR code is a two-dimensional barcode. It is also known as a matrix barcode and provides data as an identifier, locator or tracker. Typical QR codes can be read using a smartphone app or digital device and usually point towards an application or website with the required information. Quick Response codes gained popularity outside the automotive industry due to their capacity to store more information and their fast readability as compared to UPC barcodes. Today, QR codes are used for identifying items, marketing, authentication processes, product information, cashless transactions, time tracking, etc.
The QR code was invented by Masahiro Hara who worked at the Japanese company Denso Wave. The initial design of the Quick Response code was inspired by goban pieces. The initial use of the QR code was to allow high-speed component scanning for vehicle tracking during manufacturing. The widespread use of QR codes was a result of the global smartphone boom. QR codes can be used today using smartphone cameras which can scan these codes for providing users with a number of handy features. Many famous mobile apps like WhatsApp or LinkedIn use QR codes. For example, WhatsApp web is a desktop variant of the famous mobile app which allows syncing your smartphone to use the app via a desktop computer by authenticating your account using a QR code.
What are the Different Types of QR Codes?
Over the years, the QR code has evolved. There are a number of different types of QR codes with different functions and capabilities. Below is a brief explanation of the different types of QR codes and their functions.
Model 1 QR Code
This is an old version of the QR code which can code 1,167 numerals. It is similar to a model 2 code. What makes this QR code different are the bottom right and midsections in the edges of the bottom and right edges, where the additional function regions lie. Furthermore, its capability to accommodate numerals is less than a model 2 code.
Model 2 QR Code
This QR code can accommodate 7,089 numerals and is an upgrade to model 1. Model 2 QR codes come with the advantage of being read even when some parts of the code are distorted.
Micro QR Code
As is evident from the name, this is a smaller version of the QR code, with a limited size for the symbol. Micro QR codes have four different sizes, ranging from 11×11 being the smallest to the largest capable of holding 35 numeric characters.
IQR Code
This is an alternative QR code design made by Denso Wave. These codes come in both square and rectangular formats, with the capability of accommodating more information using 30% less space.
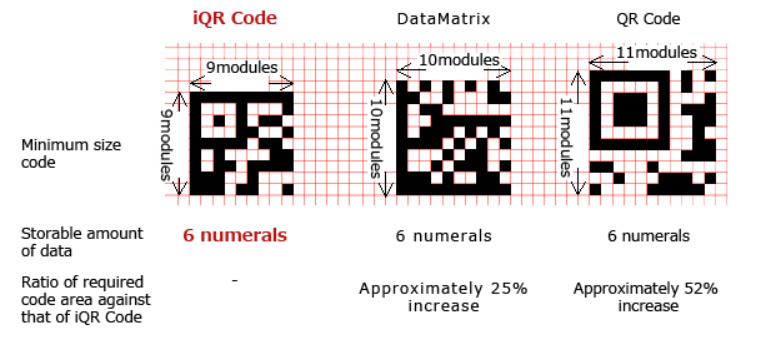
Source: qrcode.com
Secure QR code
Secure Quick Response code, Secure QR code or SQRC is the name of a type of QR code that has a private data segment. This private data segment is used for storing private information, such as for managing a company’s internal information. To decipher this QR code, an encryption key is used.
 Example of Secure QR Code
Example of Secure QR Code
Codes with QRGraphy
These QR codes come with graphical content. Such a QR code can contain different colors, logos and images. These codes come with graphical and transparent variants.
Example of QRGraphy code
Frame QR Code
The Frame QR code contains a canvas area. This area can be used for adding letters, graphics, illustrations and photos in the center of the canvas area.
JAB Code
A JAB Code is a colorful QR code with a 2D matrix symbology arranged in the form of squares or rectangle-based grids. These codes come with primary symbols and can include secondary symbols as well.
HCC2D
High Capacity Colored 2-Dimensional or HCC2D is a type that uses colors for increasing the density of the QR code. HCC2D is still relatively new and it might take some time before it can be widely used due to the various complications that the introduction of colors can cause to QR codes, such as chromatic distortions during the phase of decoding.
Different Uses of QR Codes
Since their humble beginning in 1994, QR codes have come a long way, with an ever-increasing market for their use, including transactions worth trillions taking place each year using them. For the average smartphone user, QR codes are a regular feature, with use ranging from access authentication to buying products, gathering product information, tracking packages and more.
Using QR Codes To Track Items
The original purpose of QR codes was to track vehicles during manufacturing. This function has been widely extended in recent years with QR codes being used for commercial tracking of items.
Using QR Codes To Direct Customers to Digital Content
This is perhaps the most widely used function of the QR code. Smartphone users often scan QR codes which redirect them to a website or app with more information about the product the code belongs to.
Using QR Codes Provide Product Information to Customers
Users can not only use QR codes for gathering information about an app or product online but also use apps that provide QR code scanning functionality to track products in real-time in supermarkets to see product information, such as nutrition information, country of origin, ingredients, etc.
Using QR Codes To Make Payments
In the wake of COVID-19, contactless payments have become a norm rather than the exception in many parts of the world. Many businesses are offering QR codes for making instant payments via mobile wallets for products purchased at retail outlets. While this feature has been around for a while, it is only now that many users are beginning to adopt it widely, especially in developing countries. In 2018, MercadoLibre debuted with QR code payments in Brazil and later they did in other countries in Latam. In the era of COVID, contactless payment methods like accepting payments via QR Code gained traction.
Using QR Codes To Avail Discounts
Many fast-food chains and retail outlets allow customers to scan QR codes for availing discounts. Banks often partner with multinational chains to offer discounts to their customers by scanning a QR code. For example, you might be able to get a 10% discount on a family meal at a fast-food if you have a banking app installed for a specific bank.
Using this app, you can scan the QR code at the payment counter to avail the discount. Similarly, QR codes are used in retail outlets and a number of other types of businesses to enable users to scan a QR code for availing a discount.
This is part of what’s called proximity marketing, and most proximity marketing strategies involve technologies such as beacons, NFC tags & QR Codes.
Using QR Codes In Virtual Stores
Quick Response codes are commonly found in virtual stores as a means of acquiring product information and making payments. Many online marketplaces and e-stores make use of QR codes.
Using QR Codes To Detect Counterfeits
Sometimes, you might scan a QR code, only to realize the code is redundant. This is often an indicator that the product is counterfeit with a gibberish code. QR codes are placed by companies and even governments around the world on items and products to help customers, retailers and distributors authenticate products and to identify counterfeits.
Using QR Codes To Log in or Access a Service
Many apps use QR codes to provide users a means to log in and access service by scanning a QR code to authenticate access. Google Authenticator uses QR Codes to setup new authenticator profiles in their app.
Using QR Codes To Send an Email or SMS
Email or SMS QR codes are used for sending an email or SMS after scanning a QR code. In such a case one needs to save the recipient information as a QR code and scan it to send an email or SMS.
Using QR Codes To Make a Phone Call
Using a QR code, users can scan the code, where the number stored in the code will become available for making a phone call. Phone numbers can be embedded into QR Codes using QR Code generators.
Using QR Codes As a Business Card
Since QR codes are often used for redirecting users to information, they are also used as business cards to allow others to scan and store your information on their smartphone.
LinkedIn let users display a QR Code to share their contact info with another person, instead of exchanging business cards, you can now show a QR Code which will point the other party directly to your LinkedIn profile.
Using QR Codes Joining a Wi-Fi Network
Some Quick Response codes are used for storing wireless network credentials. One can scan the QR code to connect to a Wi-Fi network. Open spaces, co-working spaces or meeting rooms can show a QR Code badge and let a guest easily join their Wifi network.
Using QR Codes As a Time-Based One-Time Password
QR codes are also used for generating Time-Based One Time Passwords or TOTP passwords after scanning a code.
Using QR Codes To Tag a Geolocation
QR codes can also be created by tagging geolocation by adding the latitude and longitude coordinates. Users can then use the code (e.g. via a geolocation app) to find the coordinates for the location.
Using QR Codes During Webinars and Presentations
There are several presentation apps that offer QR code scanning for the audience to follow the slides of the presenter real-time on their smartphones and laptops or to instantly cast their vote during a Live presentation. Want to direct your participants in a Zoom meeting to another website, a poll or take any other action? QR codes can help for this purpose. By embedding an URL in a QR Code, you can show your participants a QR Code during the live presentation and let them take any desired action.

Presenters can also allow entire PowerPoint presentations to be downloaded after someone from the audience scans a QR code. This can help the audience acquire a copy of the presentation or handouts by downloading it after scanning a code. Such a code might be made available at the start of the presentation by displaying it on the monitor or through a webpage.
Another practical use of QR Codes is for polls. Participants in a webinar, conference or presentation can scan a QR Code and automatically open a presentation poll that is tailored for that specific event.
Reasons for Boom of QR Codes in Times of COVID-19
QR code usage in the USA is estimated to be 11 million in 2020, which is likely to increase due to COVID-19. In 2016, it was estimated that transactions worth $1.65 trillion took place in China using QR codes. According to Juniper Research, by 2022 1 billion users are expected to have access to QR codes via smartphones, with an estimated 5.3 billion QR code coupons redeemed. But the boom in QR codes in times of COVID-19 doesn’t even require market research to visualize its growth. Today, QR codes are everywhere, be it supermarkets, when buying airline or movie tickets, at payment counters in famous restaurant chains, at online retailers and social media websites, etc.

There are currently two major factors which can be considered as the reason for the growth of QR codes. One is the ease of use, which does not require typing lengthy passwords and user information and the second is the rise in contactless services due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Since the novel Coronavirus is suspected to spread via surface to surface contact and social distancing protocols bar people from cash counters without necessary precautions (e.g. a counter with a glass shield), contactless payments are easy and convenient to make using Quick Response codes. Furthermore, the use of QR codes even eliminates the need for using credit or debit cards, further reducing the need for a surface to surface contact and enabling end-users to enjoy social distancing. Even when making payments online, QR codes scanned via banking mobile apps is easier than entering debit or credit card credentials for logging into an account to make a payment.
Final Words
QR codes have always had the potential for expanding into different sectors due to their ease of use, the capability of storing data in small spaces and security features. In the wake of the spread of COVID-19, people are likely to remain cautious for the foreseeable future in making cash-based payments.
QR codes offer a convenient way of reducing surface to surface contact which is most likely to spread the Novel Coronavirus, i.e. through currency notes or contact via payment counters. While the transmissibility of the virus through such modes is still up for debate, social distancing and contactless payment are still considered one of the precautions likely to prevent the virus, along with wearing masks and frequent handwashing and use of hand sanitizers. You can also read Beaconstac’s article about Static vs. Dynamic QR Codes: Differences, Benefits, and What to Choose.
Due to the paradigm shift caused by COVID-19, we are seeing a growth of innovative ideas and a new way people do business. As customers and businesses evolve in the wake of the new world being shaped by increased caution, QR codes are likely to experience a boom and integrate as a part of our daily lives in ways we might not have thought possible.
For more information, check our article about how to insert a QR Code in PowerPoint.


